The Role Of Windows In Building Envelope Design
May 26, 2016 By Fenesta
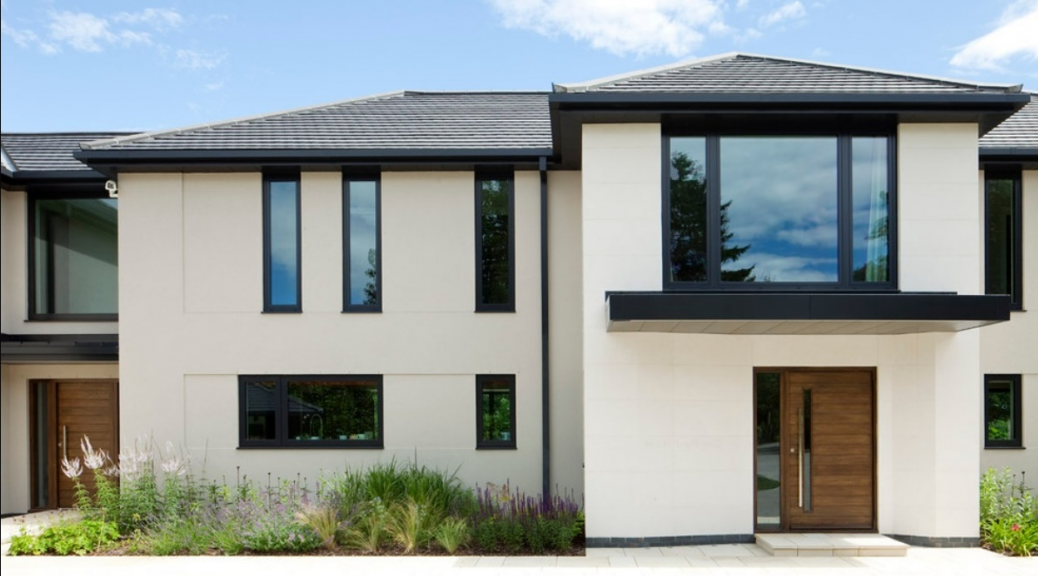

Creating for your home the ideal interface with the outside environment
Buildings are a work of art; right from the foundation to the minute decor, they require every bit of planning. Light, wind, heat, water and sound are all forms of energy that interact with a building’s environment exchanging matter and energy in the process. Architects and engineers plan and study the building’s design and surroundings to develop the best conditions for its occupants.
Windows, being part of a building’s fenestration, massively influence the structure’s envelope design. They come in various styles, sizes, materials and combinations thereof. To make the best of windows, it is important to know how they contribute to boosting the energy efficiency of the building’s enclosure. Here is a guide to the building’s envelope design and the role played by windows in enhancing it.
 An interface between the outside and inside world
An interface between the outside and inside world
Components of Building Envelope
The part of any building that separates the spatial environment of the exteriors from that of the interiors is known as an environment separator. The collection of all such environment separators for a building constitutes its envelope or enclosure.
Main components of the envelope involve - • Roof systems • Above-grade wall systems including fenestration and doors • Below-grade wall system • Base floor system In general, roof, flooring, walls, fenestration and doors make up the building’s enclosure. Main Functions of a Building Envelope • Fortifying the structure The envelope components distribute the load imposed on it by the internal and external environments. They account for support, resistance, transfer and accommodation of various forms of structural loads. • Controlling movement of energy and matter The design could be either an open-structural frame or a close shell depending on the climate, culture and available materials. A well-designed envelope responds to local climate. • Providing shelter and comfort Good buildings are known for their water penetration and air infiltration resistance. They cut off noise and allow natural light to provide extreme luxury indoors.
Role of Windows
Windows are not merely peepholes to the world outside; they also protect inhabitants from the elements. While good windows shield you from natural forces, best windows enable optimal use of indoor energy sources. Windows play many roles in the building’s enclosure design and therefore are a major influence on its envelope. They add to the building’s aesthetics and extend power-saving capabilities to the envelope. By optimizing energy utility indoors, they promote greener lifestyles.
Optimizing Efficiency of Windows
Glazing
Be it transparent or translucent layers, glazing of windows effectively influences the thermal and visual comfort of a space. Good glazing properties are important because they affect the amount and quality of daylight along with the amount of solar heat gain that is permitted into the building. It allows visible light into the room, air infiltration, condensation, acoustic damping, and distribution of light angles.

High-performance Windows
Windows that have low rate of loss of heat, U-factor, hence better resistance to heat, are better insulators and more efficient. Such uPVC windows lower energy costs involved in maintaining optimal temperatures indoors and reduce the heating, ventillation and air-conditioning (HVAC) expenses. By controlling natural light transmission and solar heat transfer indoors it improves the visual and thermal comfort inside the building.
Many factors are involved while considering the performance of windows in the building’s envelope design. U-factor, Solar Heat Gain Co-efficient (SHGC), visible transmittance and condensation resistance are the quantifiable properties to determine the most effective type of window for the climate in your locality and environment conditions










Comments