Your Guide to Understanding Safety Glass
May 16, 2019 By Fenesta

Knowing different types of safety glasses and their characteristics can help you in selecting the right one based on your needs.

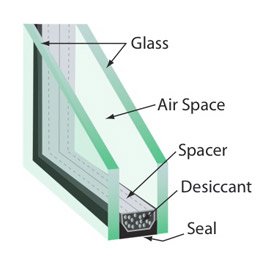
As the name suggests, safety glasses are specifically designed to possess higher mechanical strength and stronger impact resistance. When compared to standard glass types, safety glasses are less likely to break or inflict injury when broken. Safety glasses also come in certain grades that are designed for fire resistance. Some of the standard types of safety glass include tempered glass, wire glass and laminated glass. Safety glasses are often preferred by people for their anti-burglar and fireproof functions. By bringing different glass plates into use, safety glasses can also be installed in a decorative way.
-
Strengthening of Glass
Two basic ways of strengthening safety glasses are – heat strengthening and tempering. Heat-strengthened glass is cooled at a rate faster than that of regular annealed glass, while tempered glass is cooled at a rate faster than that of heat-strengthened glass. Using more than one lite of glass in application is one of the ways to strengthen glass. Laminated safety glass, for instance, constitutes of two or more lites of glass combined together by a plastic layer. Heat-strengthened glass is produced by heating annealed glass evenly and then cooling it at a slow rate. The rate at which the glass is cooled directly influences its strength. Heat-strengthened glass is two times as strong as regular annealed glass (of the same thickness and size), which makes it more resistant to impacts and wind loading. Upon breaking, this glass cracks into big, jagged pieces just like annealed glass. Heat-strengthened glass is normally used in high-rise buildings to aid in thermal stress resistance. However, since heat-strengthened glass breaks into large pieces, it does not qualify for safety glazing materials. As per building codes, safety glazing is essential for commercial doors, storefronts and shower doors owing to safety reasons.
-
Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is manufactured by layering polyvinyl butyral in between two or more lites of glass. After this, the unit is fused under pressure and heat in an autoclave, which is a special oven. The thickness of laminated glass can range from 0.015 inches to 0.090 inches, and it can either be clear or tinted. The process of laminating the glass can be carried out on tinted, clear, heat-strengthened, reflective or tempered glass. Even though laminated glass is brought into use for safety glazing applications, it has various other functions as well, which include sound reduction, burglar resistance, space enclosures and sloped glazing. When laminated glass breaks, its particles stick to PVB and do not fall or fly. Vehicle windshields are often made by packing a layer of laminate in between two layers of glass.
-
Tempered Glass
Also recognized as toughened glass, this glass is produced by uniformly heating annealed glass. Following this, the glass is swiftly and evenly cooled by blowing air onto both the surfaces at the same time. The swift cooling intensifies the compression on the surface, and tension inside the glass. The thickness of tempered glass can range from 1/8 inches to ¾ inches. Tempering increases the tensile strength or bending of the glass. That is why tempered glass is four times as strong as annealed glass of similar thickness and size. Tempered glass can therefore resist forces caused by wind, heat and impact better. Further, tempered glass has greater resistance to deflection and wind in comparison to heat-strengthened glass. Upon breaking, the glass shatters into small pieces, thus reducing the chances of serious injuries to people around.
-
Wire Glass
Wire glass, another type of safety glass, is created by inserting a welded wire net of a specific design into the molten glass before it is put in rollers. The wire here does not enhance the strength of the glass; however, if it were to shatter, it would hold the lite in the window sash. Wire glass meets more fire codes, which is why its use is preferred in fire-rated windows. Wired glass, anyhow, cannot be tempered and has only half the strength of annealed glass of similar thickness. A few other types of safety glass include bullet-resistant glass and frosted glass. Bullet-resistant glass is created by bringing several layers of laminate and glass into use. Frosted glass on the other hand has the property of translucence which blurs images while still allowing light inside a space.









Comments